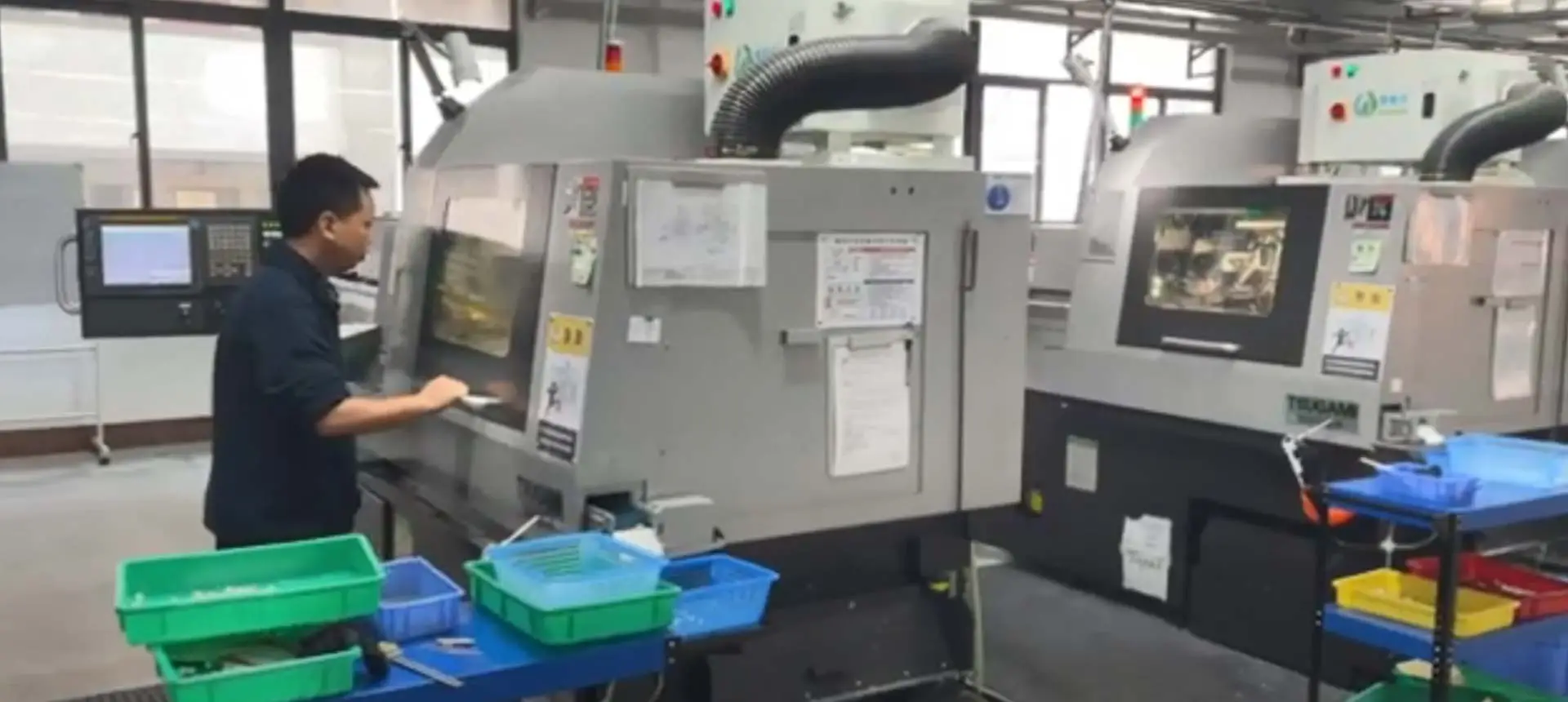
Dans notre entreprise, nous utilisons un processus très efficace pour produire des pièces d'usinage CNC qui répondent aux exigences spécifiques de nos clients. Voici un aperçu du processus que nous suivons:
Conception et programmation: Nos ingénieurs qualifiés travaillent avec le dernier logiciel pour concevoir et programmer la pièce, en veillant à ce qu'elle réponde aux spécifications et aux tolérances requises.
Sélection du matériau: Nous sélectionnons avec soin le matériau approprié pour la pièce, en tenant compte de sa résistance, de sa durabilité et d'autres propriétés.
Usinage CNC: Nous utilisons des machines avancées contrôlées par ordinateur pour effectuer le processus d'usinage CNC, qui consiste à éliminer l'excès de matériau de la pièce pour créer la forme finale de la pièce.
Inspection de qualité: Notre équipe inspecte les pièces à chaque étape du processus, en utilisant les dernières technologies et équipements pour s'assurer que chaque partie répond aux normes de qualité requises.
Finition: Nous offrons une gamme d'options de finition, y compris le sablage, le polissage, l'anodisation et le revêtement, pour améliorer l'apparence et la fonctionnalité des pièces.
Emballage et expédition: Nous emballons soigneusement les pièces pour assurer leur arrivée en toute sécurité et les livrons rapidement à nos clients.
Grâce à notre engagement envers la qualité, l'efficacité et la satisfaction du client, nous nous sommes forgé une réputation de fournisseur de confiance de pièces d'usinage CNC personnalisées. Si vous avez un projet qui nécessite des pièces d'usinage CNC de haute qualité, veuillez nous contacter pour discuter de vos besoins et de la façon dont nous pouvons vous aider.
Description | Fraisage CNC | Tournage CNC |
Matériaux | Aluminium/Cu/acier/inoxydable | Aluminium/Cu/acier/inoxydable |
Taille maximale de la pièce | 1000mm * 1000mm * 600mm | 1000mm * 600mm * 600mm |
Délai standard | 4 jours ouvrables | 4 jours ouvrables |
Tolérance (± mm) | Fraisage seulement: jusqu'à ± 0.025mm Avec la coupe de fil ou EDM: jusqu'à 0.002mm | Jusqu'à ± 0.0025mm |
Assurance qualité | ISO 9001, ISO 45001:2018 Audits des fournisseurs CMM et projecteur de mesure 2D Rapports d'inspection Inspection fonctionnelle Échantillonnage personnalisé | ISO 9001, ISO 45001:2018 Audits des fournisseurs CMM et projecteur de mesure 2D Rapports d'inspection Inspection fonctionnelle Échantillonnage personnalisé |
Haute précision et précision: avec l'usinage CNC, les pièces peuvent être fabriquées avec des tolérances extrêmement serrées et une précision élevée, offrant un niveau de cohérence difficile à atteindre avec les processus d'usinage manuel.
Large gamme de matériaux: L'usinage CNC peut être utilisé avec une variété de matériaux, y compris le métal, le plastique, le bois et les composites.
Rentable pour la production à grand volume: l'usinage CNC est idéal pour la fabrication à grand volume car il permet la production de grandes quantités de pièces à un coût par pièce inférieur.
Efficacité accrue: La nature automatisée de l'usinage CNC signifie que la production peut être réalisée plus efficacement, sans intervention manuelle, ce qui permet des temps de production plus rapides.
Polyvalence: l'usinage CNC peut être utilisé pour produire des composants complexes avec des formes et des géométries complexes, ce qui le rend adapté à une large gamme d'applications.
Dans le domaine de la fabrication de précision, l'usinage à commande numérique par ordinateur (CNC) se présente comme une merveille technologique qui a révolutionné l'industrie de la production. L'usinage CNC implique l'utilisation de systèmes informatisés pour contrôler les machines-outils et les processus, permettant une production très précise et efficace de pièces et de composants complexes. Les différents processus d'usinage CNC sous HHC ont des étendues d'application et des caractéristiques de traitement différentes. Ce qui suit fournit une classification et une introduction détaillées.
L'un des types d'usinage CNC les plus courants, le fraisage utilise des outils de coupe rotatifs pour enlever le matériau d'une pièce. La fraiseuse peut se déplacer le long de plusieurs axes, créant une large gamme de formes, de fentes et de trous. Des composants simples aux prototypes complexes, le fraisage est polyvalent et largement utilisé dans des industries telles que l'aérospatiale, l'automobile et l'électronique.
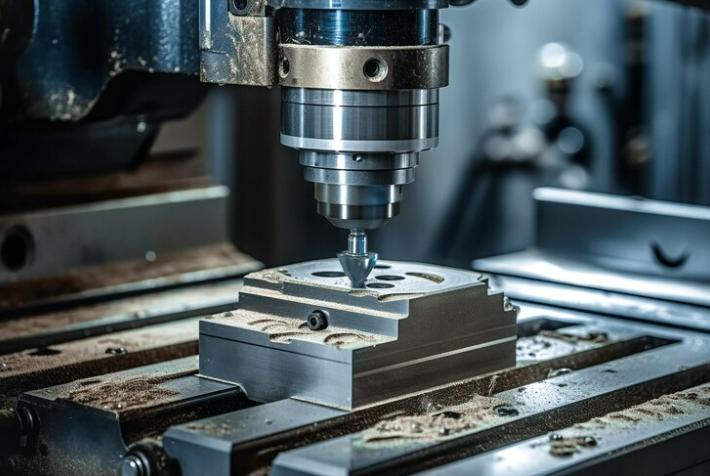

Lors des opérations de tournage, la pièce tourne tandis qu'un outil de coupe la façonne dans la forme souhaitée. Ce type d'usinage CNC est idéal pour créer des composants cylindriques tels que des arbres, des boulons et des broches. Le tournage de précision est une pierre angulaire des processus de fabrication, offrant efficacité et précision pour diverses applications.
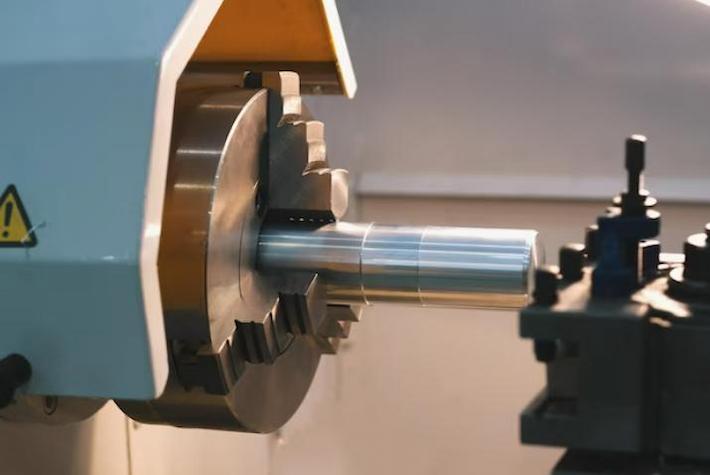

Comme son nom l'indique, les machines CNC de forage sont conçues pour créer des trous dans les pièces. Ces machines utilisent des forets rotatifs pour enlever le matériau, et ils sont cruciaux dans la production de composants qui nécessitent des trous précis et uniformes. Des industries comme la construction, le travail des métaux et l'électronique dépendent fortement du forage CNC pour leurs besoins de fabrication.
Lorsque l'extrême précision et la finition de surface sont primordiales, le meulage CNC entre en jeu. Cette méthode utilise des roues abrasives pour éliminer le matériau et obtenir des tolérances serrées. Le meulage CNC est indispensable dans la production d'outils, de moules et de composants de haute précision utilisés dans les dispositifs médicaux et l'ingénierie aérospatiale.
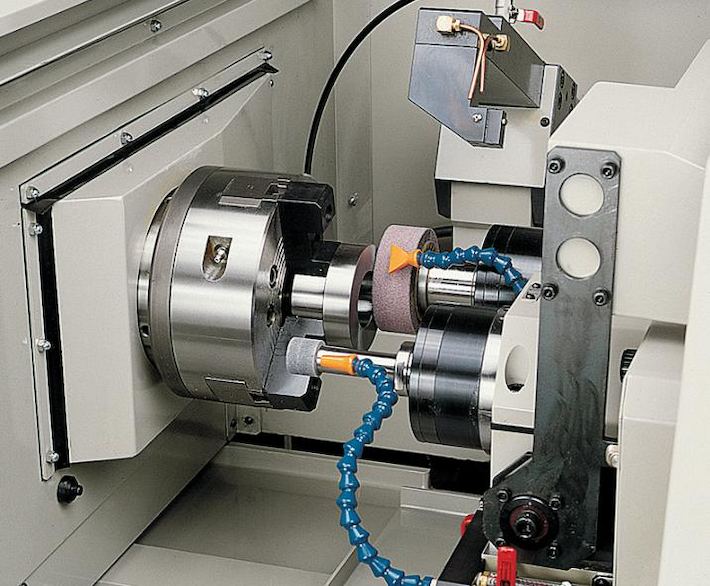

L'EDM est une méthode d'usinage CNC non traditionnelle qui utilise des décharges électriques pour façonner des matériaux. Grâce à des étincelles électriques soigneusement contrôlées, l'EDM peut créer des formes complexes et complexes avec une grande précision. Cette technique est particulièrement utile pour les métaux durs qui sont difficiles à usiner avec des méthodes traditionnelles. Par exemple, nous utilisons l'usinage électrique de décharge (EDM) pour personnaliser les modèles pour les moules

La découpe laser CNC implique l'utilisation d'un faisceau laser pour couper les matériaux, créant des bords précis et propres. Cette méthode est largement utilisée dans la fabrication de composants en tôle pour des industries allant de l'automobile à l'électronique grand public. Le haut niveau de précision et de vitesse fait de la découpe laser CNC un processus inestimable dans la fabrication moderne.

Dans le paysage en constante évolution de la fabrication, deux technologies de pointe sont devenues les pionniers: l'usinage CNC et l'impression 3D. Chaque méthode apporte son propre ensemble de forces et d'applications à la table. Plongons dans les subtilités de l'usinage CNC et de l'impression 3D, en comparant leurs caractéristiques, avantages et limites.
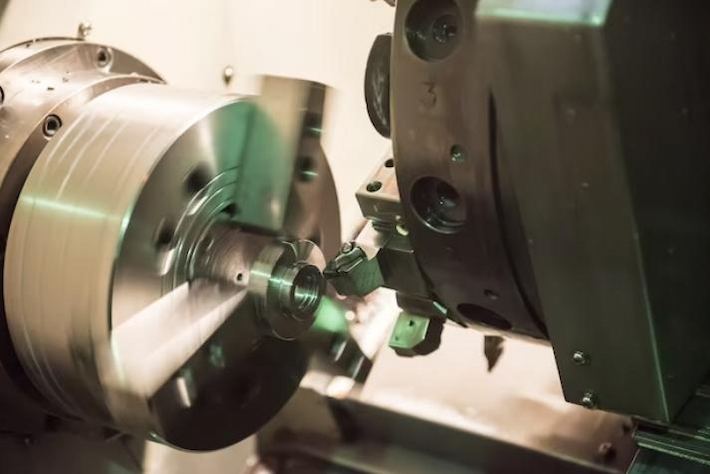

L'usinage CNC (Computer Numerical Control) est un processus de fabrication soustractive. Il s'agit d'enlever du matériau d'une pièce pour obtenir la forme souhaitée. Ce processus utilise des logiciels de conception assistée par ordinateur (CAO) et de fabrication assistée par ordinateur (FAO) pour contrôler avec précision le mouvement des outils de coupe.
L'usinage CNC est réputé pour son haut niveau de précision et de précision. Il peut atteindre des tolérances serrées et produire des détails complexes, ce qui le rend approprié pour les applications où la précision est primordiale, comme l'aérospatiale et les industries médicales. L'usinage CNC est polyvalent en matière de compatibilité des matériaux. Il peut gérer une large gamme de matériaux, y compris les métaux, les plastiques et les composites. Cela en fait un choix préféré pour les industries exigeant la durabilité et la résistance de leurs composants. L'usinage CNC est bien adapté au prototypage et à la production à grande échelle. Bien que le temps d'installation pour l'usinage CNC puisse être plus long que l'impression 3D, il excelle dans la production de pièces fonctionnelles de haute qualité. L'usinage CNC offre une finition de surface supérieure par rapport à de nombreuses technologies d'impression 3D. Cela en fait un choix idéal pour les composants nécessitant une surface polie ou lisse.
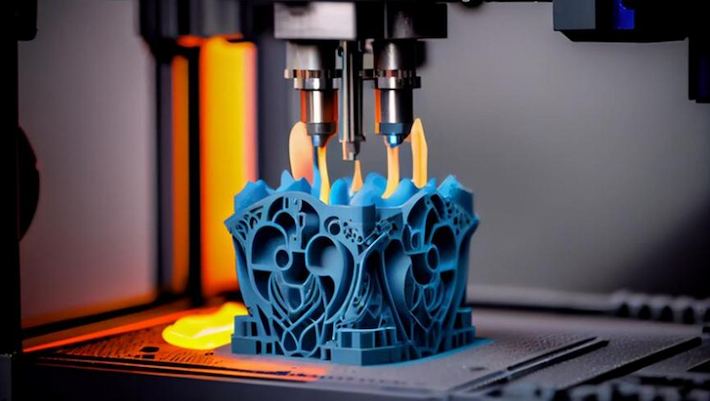

L'impression 3D, ou fabrication additive, construit des objetsCouche par couche à partir d'un modèle numérique. Il s'agit de déposer du matériel dans un motif spécifique pour créer un objet tridimensionnel. Ce processus est très polyvalent et permet des géométries complexes.
L'impression 3D prend en charge une gamme diversifiée de matériaux, y compris les plastiques, les métaux, la céramique et même les bio-matériaux. Les choix de matériaux continuent de s'étendre, ouvrant de nouvelles possibilités pour diverses industries. L'impression 3D excelle dans le prototypage rapide et est bien adaptée aux géométries complexes qui peuvent être difficiles pour l'usinage CNC. Cependant, il peut ne pas correspondre à la vitesse d'usinage CNC pour la production à grande échelle. En termes de rapport coût-efficacité, en particulier pour la production et le prototypage à faible volume, l'impression 3D peut offrir des avantages en raison de la réduction du gaspillage de matériaux et des configurations plus simples. L'impression 3D est célébrée pour ses capacités de personnalisation. Il permet la création de conceptions uniques et personnalisées sans avoir besoin d'outillage supplémentaire, ce qui le rend idéal pour la production unique ou en petits lots.
Dans l'ensemble, le choix entre l'usinage CNC et l'impression 3D dépend de facteurs tels que les matériaux, les exigences de précision, l'échelle de production et la complexité du projet. Pour des séries de production plus importantes, l'usinage CNC excelle dans la précision et la polyvalence des matériaux, tandis que l'impression 3D brille dans le prototypage rapide et les applications de conception complexes.
Cations.
L'usinage CNC (Computer Numerical Control) joue un rôle crucial dans la fabrication de composants de précision de haute qualité. Vous trouverez ci-dessous les étapes générales du processus et les détails pour la fabrication de brides usinées CNC:

Étapes de processus pour les brides usinées CNC:
1. conception et modélisation:
Avant de fabriquer des composants CNC, la conception CAO (conception assistée par ordinateur) est essentielle. Les ingénieurs en conception utilisent un logiciel de CAO pour créer un modèle 3D de la bride, déterminant les formes géométriques, les dimensions et les chemins d'usinage.
2. préparation matérielle:
Choisissez des matières premières appropriées, généralement des métaux (tels que l'acier inoxydable, l'aluminium, etc.). La sélection du matériau dépend du but de la bride, de l'environnement de travail et des exigences de performance.
3. procédés d'usinage:
A. Roughing:
Utilisez des outils de coupe sur les machines CNC pour effectuer l'ébauche, en façonnant à peu près la forme générale de la pièce.
Le but de l'ébauche est d'éliminer rapidement l'excès de matériau, laissant une forme finale approximative.
B. Semi-finissage:
Utilisez différents outils pour semi-finir la pièce, en approchant davantage la forme finale.
Réduisez la vitesse de coupe pour améliorer la douceur de la surface.
C. Finissage:
Utilisez de petits outils pour la coupe de précision finale, en atteignant les dimensions finales et la douceur de surface.
La finition implique souvent l'utilisation d'outils plus petits pour améliorer la précision d'usinage.
D. Trou d'usinage et de coupe de fil:
Utilisez des outils spécialisés pour l'usinage des trous et le filetage pour vous assurer que la bride répond aux spécifications de conception.
4. Inspection et contrôle de qualité:
Après chaque étape d'usinage, effectuez des inspections pour vous assurer que les dimensions, la forme et la qualité de la surface de la pièce répondent aux exigences de spécification. Les méthodes d'inspection courantes comprennent la mesure coordonnée, les tests de rugosité de surface et les tests par ultrasons.
5. Traitement de surface:
Selon les exigences, effectuer des traitements de surface tels que le polissage, le sablage ou le revêtement pour améliorer l'apparence et la résistance à la corrosion.
6. emballage et livraison:
Après avoir terminé l'usinage et l'inspection, emballer les brides selon les exigences du client et procéder à la livraison.
L'usinage CNC (Computer Numerical Control) est un processus de fabrication dans lequel un logiciel informatique préprogrammé contrôle le mouvement des machines et des outils. Ce processus permet la création de pièces très précises et complexes à partir de divers matériaux, y compris les métaux et les plastiques. L'usinage CNC est largement utilisé dans des industries telles que l'automobile, l'électronique et l'aérospatiale.
La rotation CNC est idéale pour produire des pièces cylindriques ou rondes, telles que des arbres, des bagues, des vis et des broches. Il est couramment utilisé pour les composants qui nécessitent une haute précision et des surfaces lisses. Des industries telles que l'automobile, le médical et l'électronique bénéficient deChine pièces tournées en aluminium.
Recherchez un fournisseur avec une vaste expérience, des équipements modernes et un engagement fort en matière de contrôle de la qualité. Des certifications telles que l'ISO 9001 et l'IATF indiquent 16949 la conformité aux normes de l'industrie. Tenez également compte de facteurs tels que la capacité de production, les délais et les avis des clients.
Chez HHC, nous offrons des pièces de précision avec des tolérances aussi serrées que ± 0.01mm, assurant une grande précision même pour les composants les plus complexes. Notre équipement avancé nous permet de maintenir la cohérence et de répondre aux exigences spécifiques de chaque projet.
Les délais varient en fonction de la complexité et de la quantité des pièces, mais nous livrons généralement des pièces d'usinage CNC en 1 à 4 semaines. Nous offrons également des services accélérés pour les projets urgents afin d'aider nos clients à respecter des délais serrés.


